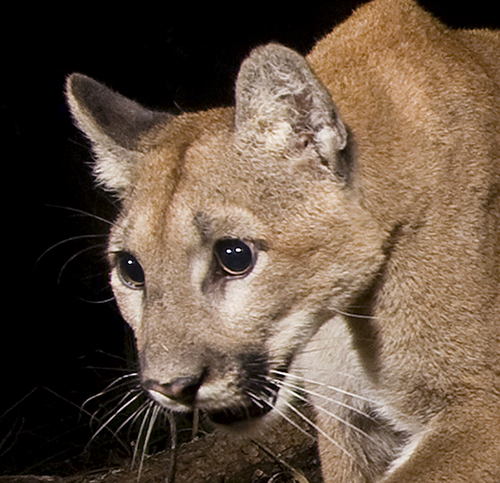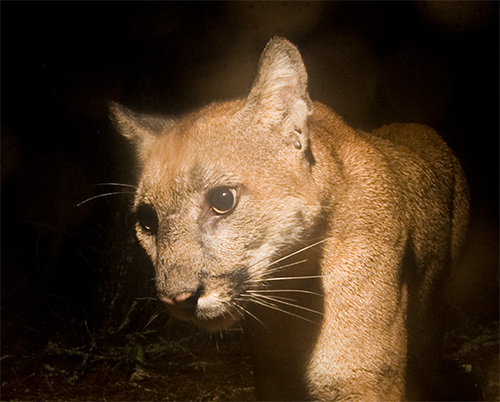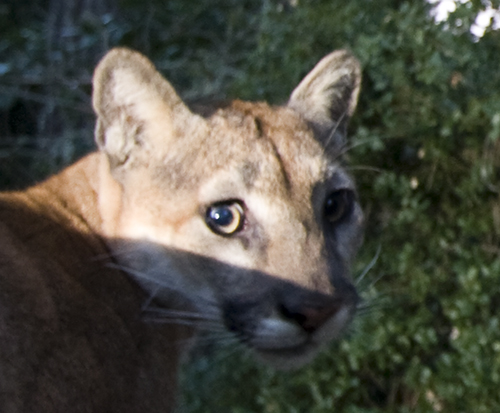
Waleed Al’Rail with Leopard Foundation’s camera trap, Hawf, Yemen
As I wrote in a previous post, using camera traps in wildlife photography provides its own unique set of challenges and possibilities for unique photographs. Using camera traps in a different country is a totally different story.
Before this assignment I was only operating one camera trap, but by the time I was getting on a plane to try and get some pictures of the mysterious wildlife Yemen has to offer they totaled five. There was surprisingly little resistance by the immigration people of Yemen to my equipment and me coming into the country. This was mainly due to the fact that I am not a journalist and even more importantly all the work David Stanton and Yousuf Mohageb had put into making this step of the project go smoothly (David is from the Foundation for the Protection of the Arabian Leopard in Yemen and Yousuf Mohageb runs Arabian Eco-tours).

David Stanton (right) and Yousuf Mohageb (center) eating dinner, Yemen
Bureaucratic problems avoided, it was time to focus on placing the cameras in spots where there were good chances of animals coming by. While Waleed Al’Rail and Murad Mohamed (both are Yemeni Arabian Leopard researchers) were checking their cameras and showing me the area, I was imagining all the good locations for the camera traps along the game trails we were using. When I expressed my ideas, Waleed and Murad made me aware of a problem I had not even considered. Yemen is a Muslim country, and in Islamic law it is not accepted to take pictures of woman. Sure that’s easy to control when you are behind the camera but when you put the camera out in nature, especially in an area like ours where people use the land and a daily basis, it is incredibly challenging. There was a fine balance between a good location for the cameras and one that women may use while they were deployed. If women saw the cameras, I was told, they would get destroyed.
Keeping this in mind, we deployed three of the five cameras into the cloud forest habitat of the Hawf Protected Area. Three days later a cyclone arrives (the worst in forty years) and destroys, or better yet, completely obliterates one of the cameras. One camera down, it was beyond repair.

Cloud forest, Hawf Protected Area, Yemen

Flooding in the Hawf Protected Area, Yemen
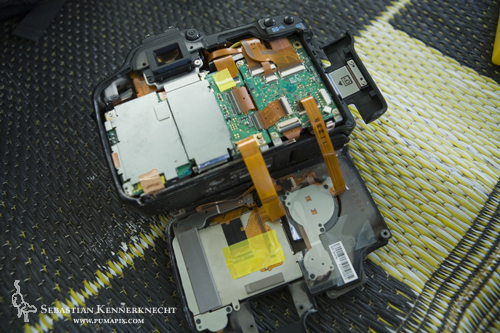
Broken camera from camera trap, Hawf Protected Area, Yemen
Nonetheless the camera captured one image before being flooded.

Honey Badger (Mellivora capensis) pair, Hawf Protected Area, Yemen
The other two cameras also snapped a few images.

Indian Crested Porcupine (Hystrix indica), Hawf Protected Area, Yemen

Arabian Caracal (Caracal caracal schmitzi), Hawf Protected Area, Yemen

White-tailed Mongoose (Ichneumia albicauda), Hawf Protected Area, Yemen

Small-spotted Gennet (Genetta genetta), Hawf Protected Area, Yemen

Honey Badger (Mellivora capensis) juvenile, Hawf Protected Area, Yemen
After a couple of weeks we placed the two remaining cameras into the far desert inlands. Animal densities are definitely lower in this area but a few different animal species are present there as well.

Desert, Hawf Protected Area, Yemen

Arabian Wolf (Canis lupus arabs), Hawf Protected Area, Yemen

Rock Hyrax (Procavia capensis), Hawf Protected Area, Yemen

Spiny Mouse (Acomys cahirinus), Hawf Protected Area, Yemen
Throughout camera trapping in Yemen I was surprised by the lack of camera trapping results. It was quite interesting how much more wary the animals are of foreign objects here, I think caused by the constant human pressure on them. As you can see from the pictures as well, most wear taken at night. Animals in Yemen are more nocturnal than in areas where hunting pressures are not as strong. While I was there I heard three live rounds go off, no doubt each time the rifle was aimed at an animal.

Now if only this was an Arabian Leopard
*If you are interested in purchasing any of the pictures displayed in this post, please check out my fine prints page for pricing.*































